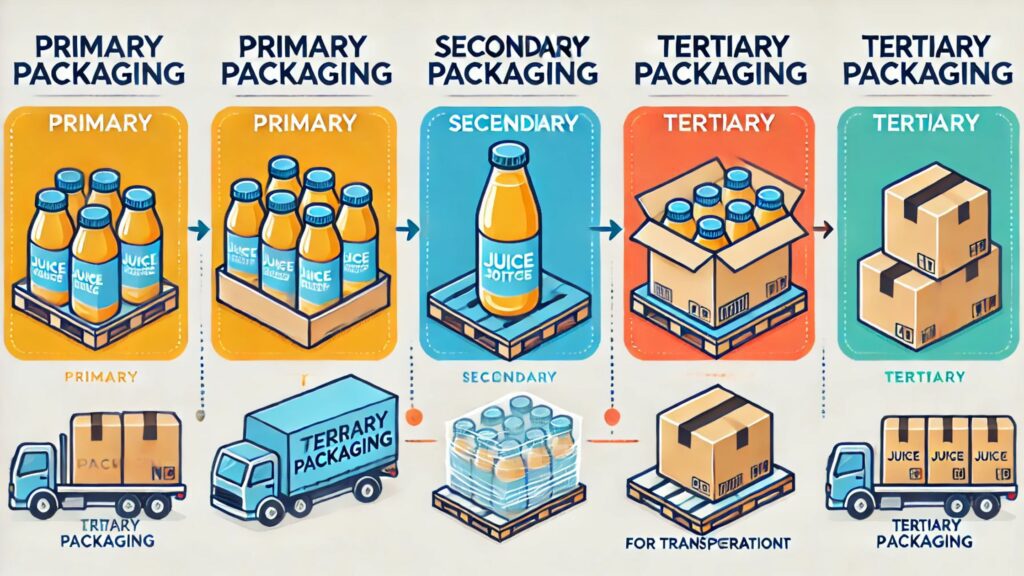
Primary Secondary and Tertiary Packaging: Packaging plays a crucial role in the storage, transportation, and protection of products. It is typically categorized into three levels: primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging. Each serves a specific purpose in the supply chain, ensuring that products reach consumers safely and efficiently.
Understanding Primary Secondary and Tertiary Packaging
Primary Packaging
Primary packaging is the first layer of packaging that directly encloses the product. It serves as a protective barrier and often includes branding elements to attract consumers. This type of packaging ensures product integrity and can also provide convenience in handling and usage.
Examples of Primary Packaging:
- Bottles for beverages and pharmaceuticals
- Sachets for food items like ketchup
- Blister packs for tablets
- Tetra packs for milk and juice
Primary packaging is designed to preserve the product’s quality, prevent contamination, and provide essential information such as ingredients, expiration dates, and usage instructions.
Secondary Packaging
Secondary packaging is the layer that groups multiple primary packages together. It provides additional protection, facilitates handling, and often serves branding and marketing purposes. This type of packaging is essential for organizing products for retail display and distribution.
Examples of Secondary Packaging:
- Cardboard boxes holding multiple bottles
- Shrink wrap around beverage cans
- Display trays for snack items
- Cartons for cosmetic products
Secondary packaging is crucial for logistics, making it easier to transport and store products in bulk while maintaining brand visibility.
Tertiary Packaging
Tertiary packaging is the outermost layer used for bulk handling, shipping, and warehouse storage. It ensures the safe transportation of goods from manufacturers to retailers and is designed to withstand the rigors of logistics operations.
Examples of Tertiary Packaging:
- Pallets stacked with multiple secondary packages
- Large shipping containers
- Stretch-wrapped loads for stability
- Corrugated fiberboard boxes used for bulk shipments
Tertiary packaging is primarily functional rather than aesthetic, focusing on efficiency and damage prevention in the supply chain.
The Importance of Packaging in Supply Chain Management
Each level of packaging plays a vital role in product safety, transportation, and presentation. Proper packaging design minimizes damage, reduces waste, and improves efficiency in logistics. Additionally, sustainable packaging solutions are becoming increasingly important as companies strive to reduce their environmental footprint.
By understanding primary secondary and tertiary packaging, businesses can optimize their packaging strategies to enhance product protection, improve cost efficiency, and strengthen brand identity.
Do you have questions about packaging strategies for your business? Share your thoughts in the comments!
Related Articles
- The Art and Science of Packaging | Trends, History & Future
- Tertiary Packaging Examples: Understanding Its Role in Logistics
- What is Tertiary Packaging? Definition, Purpose, and Benefits
- The Importance of Secondary Packaging Material in Modern Supply Chains
- Secondary Packaging Examples: Enhancing Protection and Presentation
- Primary and Secondary Packaging: Understanding Their Roles and Importance
- The Importance of Secondary Packaging Machinery in Modern Manufacturing
- Secondary Packaging in Pharmaceutical Industry: Importance & Innovations
- What Is Secondary Packaging? The Essential Guide for Businesses
- The Ultimate Guide to Popcorn Packaging: Innovation, Trends, and Sustainability