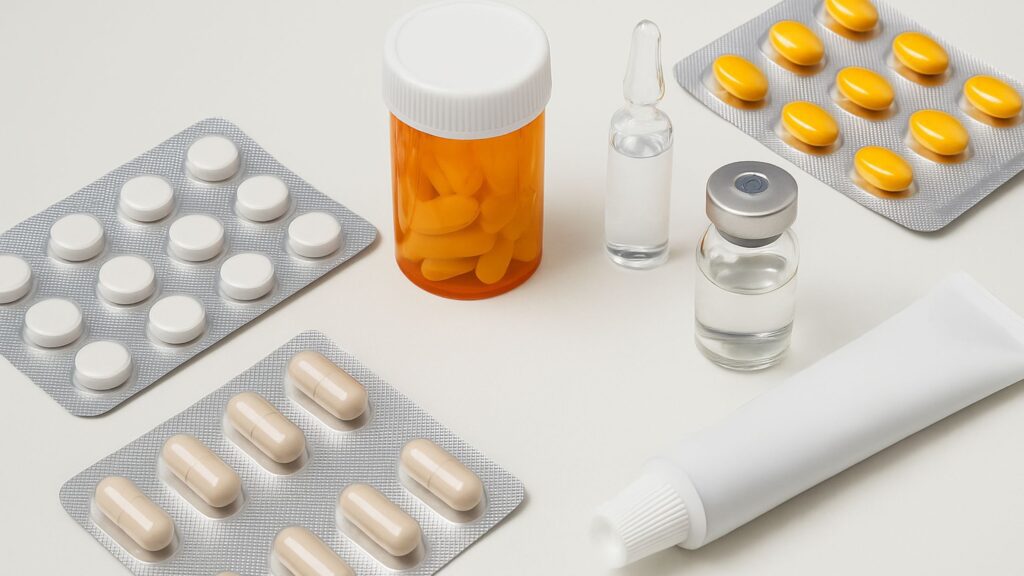
Primary Packaging Pharmaceutical Products: In the pharmaceutical industry, packaging is not just a matter of presentation—it’s a critical component of product integrity, safety, and efficacy. One of the most vital aspects of this process is primary packaging pharmaceutical products. This blog post delves deep into what primary packaging entails, its importance, types, materials, regulatory considerations, and recent innovations in the field.
What is Primary Packaging in Pharmaceuticals?
Primary packaging refers to the material that first envelops the pharmaceutical product and holds it. This is the packaging that is in direct contact with the drug, whether it’s a solid, liquid, or gas. The primary goal is to protect the product from contamination, degradation, and physical damage.
Key Functions of Primary Packaging
-
Protection: Guards the product from environmental factors such as moisture, oxygen, light, and temperature.
-
Containment: Ensures that the product stays within the packaging without leakage or loss.
-
Preservation: Maintains the chemical and physical integrity of the drug.
-
Identification: Enables labeling and product information that ensures traceability and regulatory compliance.
-
Patient Safety: Ensures tamper-evident features and child-resistant mechanisms.
Without adequate primary packaging, even the most effective drug formulations can become ineffective—or worse, unsafe.
Common Types of Primary Packaging for Pharmaceutical Products
The type of primary packaging used largely depends on the nature of the pharmaceutical product—whether it’s a tablet, capsule, injection, or topical formulation. Here’s an overview of the most commonly used primary packaging formats:
1. Blister Packs
Blister packs are widely used for solid dosage forms like tablets and capsules.
-
Pros: Tamper-evident, individual unit-dose packaging, good barrier properties.
-
Materials: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), PVDC (Polyvinylidene Chloride), Aluminum foil.
-
Applications: Oral drugs, OTC medications, and clinical trial samples.
2. Bottles
Bottles—made from glass or plastic—are typically used for liquids, capsules, and tablets.
-
Pros: Reusable, resealable, can accommodate large quantities.
-
Materials: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), Glass (Type I, II, III).
-
Applications: Liquid syrups, oral solids, and bulk packaging.
3. Ampoules
Ampoules are small sealed vials used to contain and preserve a sterile pharmaceutical product.
-
Pros: Hermetically sealed, ideal for single-use sterile liquids.
-
Materials: Glass, sometimes plastic.
-
Applications: Injectable drugs, vaccines, anesthetics.
4. Vials
Similar to ampoules but resealable, vials are used for liquid and freeze-dried injectable drugs.
-
Pros: Can be resealed, compatible with rubber stoppers.
-
Materials: Borosilicate glass, plastic polymers.
-
Applications: Antibiotics, vaccines, biologics.
5. Syringes and Cartridges
Pre-filled syringes and cartridges are gaining popularity due to convenience and accuracy.
-
Pros: Accurate dosing, reduced contamination risk.
-
Materials: Glass or polymer-based.
-
Applications: Insulin, biologics, emergency medications.
6. Tubes
Tubes are used for topical applications like creams, ointments, and gels.
-
Pros: Flexible, easy dispensing, hygienic.
-
Materials: Aluminum, plastic laminates.
-
Applications: Dermatological and ophthalmic drugs.
Materials Used in Primary Packaging Pharmaceutical Products
Material selection is a crucial step in primary packaging. The materials must be inert, impermeable, and compliant with regulatory standards.
Glass
-
Types:
-
Type I: Borosilicate glass (high resistance)
-
Type II: Treated soda-lime glass
-
Type III: Regular soda-lime glass
-
-
Applications: Injectable drugs, biologicals.
Plastics
-
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Resistant to moisture and chemicals.
-
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): High clarity, strong barrier.
-
PP (Polypropylene): High melting point, used in autoclaving.
Aluminum
-
Often used in blister packs and tubes due to its barrier properties and durability.
Regulatory Requirements for Primary Packaging Pharmaceutical Products
Compliance is non-negotiable in pharmaceutical packaging. Regulatory bodies worldwide have strict guidelines governing primary packaging pharmaceutical products.
Key Regulatory Agencies
-
FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration): 21 CFR Part 211
-
EMA (European Medicines Agency): EU GMP Guidelines
-
ICH (International Council for Harmonisation): Q1A (Stability), Q3C (Impurities)
-
USP (United States Pharmacopeia): <661> (Containers), <671> (Permeability), <381> (Elastomeric closures)
Key Testing & Compliance Factors
-
Extractables and Leachables: Ensure no harmful substances migrate into the drug.
-
Sterility: Especially for injectable packaging.
-
Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR): Important for hygroscopic drugs.
-
Light Transmission: Protect photosensitive drugs.
Primary Packaging and Drug Stability
The interaction between a drug and its primary packaging can significantly affect shelf life. Packaging must be designed to maintain the stability of the drug throughout its lifecycle.
Stability Study Considerations
-
Accelerated Conditions: Evaluate how packaging performs under stress.
-
Real-Time Studies: Determine true shelf life under normal conditions.
-
Compatibility Studies: Assess chemical interaction between drug and packaging material.
Innovation and Trends in Primary Packaging Pharmaceutical Products
The pharmaceutical packaging industry is rapidly evolving. Here are some exciting trends shaping the future:
1. Smart Packaging
Smart packaging integrates sensors, indicators, or electronics that can:
-
Track temperature excursions.
-
Monitor tampering or counterfeiting.
-
Provide patient adherence data.
2. Sustainable Materials
Sustainability is increasingly important. Innovations include:
-
Biodegradable polymers
-
Recyclable blister packs
-
Lightweight glass alternatives
3. Customization and Personalization
With the rise of personalized medicine, there’s a growing need for customized packaging that supports:
-
Small batch sizes
-
Flexible labeling
-
Unique serialization
4. Pre-Filled Delivery Systems
Demand for ready-to-administer medications is driving growth in:
-
Pre-filled syringes
-
Auto-injectors
-
Pen injectors
These innovations not only enhance patient convenience but also reduce dosage errors and contamination risks.
Challenges in Primary Packaging Pharmaceutical Products
Despite its critical role, primary packaging faces several challenges:
-
Cost Pressures: High-quality materials and compliance testing are expensive.
-
Material Shortages: Especially during global crises like pandemics.
-
Regulatory Variability: Differing global standards complicate packaging design.
-
Complex Biologics: Require highly specialized, often temperature-sensitive packaging.
Best Practices for Selecting Primary Packaging
Here are some practical tips to ensure optimal primary packaging for pharmaceutical products:
-
Start Early: Include packaging design during early formulation stages.
-
Conduct Compatibility Testing: Evaluate drug interaction with packaging material.
-
Focus on User Needs: Consider ease of use, accessibility, and patient compliance.
-
Ensure Supply Chain Robustness: Work with reliable packaging partners.
-
Stay Compliant: Regularly audit regulatory updates and ensure alignment.
Final Thoughts: Primary Packaging Pharmaceutical Products
Primary packaging pharmaceutical products play a crucial, multifaceted role in the drug delivery process. From ensuring product integrity to improving patient outcomes, the importance of selecting the right primary packaging cannot be overstated. As the industry continues to evolve with new technologies, sustainability goals, and patient-centric solutions, the future of primary packaging looks both dynamic and promising.
Whether you’re a manufacturer, regulatory professional, or supply chain specialist, understanding the nuances of primary packaging pharmaceutical products is essential for success in the pharmaceutical sector.
Related Articles
- Primary Packaging of Toothpaste: Materials, Design, and Innovation
- Primary Packaging of Tea: Ensuring Freshness, Flavor, and Functionality
- Primary Packaging of Tablets: Types, Materials, and Best Practices
- Primary Packaging of Soap: Everything You Need to Know
- Primary Packaging of Shoes: Protecting Style from Factory to Footwear Shelf
- Primary Packaging of Shampoo: Types, Materials & Innovations Explained
- Primary Packaging of Samsung Mobile Phones: Design, Innovation, and Sustainability
- Primary Packaging of Perfume: A Deep Dive into Design, Function & Innovation
- Primary Packaging of Noodles: Materials, Functions, and Innovations
- Primary Packaging of Milk: Materials, Methods, and Innovations